Table of contents
- Shared and changing security responsibility
- Building security in every stage of the cloud is a need.
- Why Cloud Security is Important for Businesses
- Main Risks Associated with Cloud Computing Security
- What are the Benefits of Cloud Security?
- What kinds of tools are required to secure a cloud environment?
- What are cloud security best practices?
- Future of cloud
- Simplifying security in complex cloud setups is the ultimate goal of cloud security
Cloud security has become a critical requirement for organizations in the digital era. The growing adoption of cloud technology has led organizations to store more and more sensitive data in the cloud, making cloud security increasingly important. Complex cloud environments, where organizations use multiple cloud providers and services to meet their specific business needs, have made it increasingly more work to manage security across these environments.
In addition, the rise of sophisticated cyber-attacks and threats means that organizations must be prepared to protect their sensitive data and systems in a cloud environment. As organizations expand globally, they must comply with many regulations and standards, making cloud security a requirement for meeting these obligations. With cloud security, organizations can take advantage of the different pricing models and services each cloud provider offers, reducing their overall security costs.
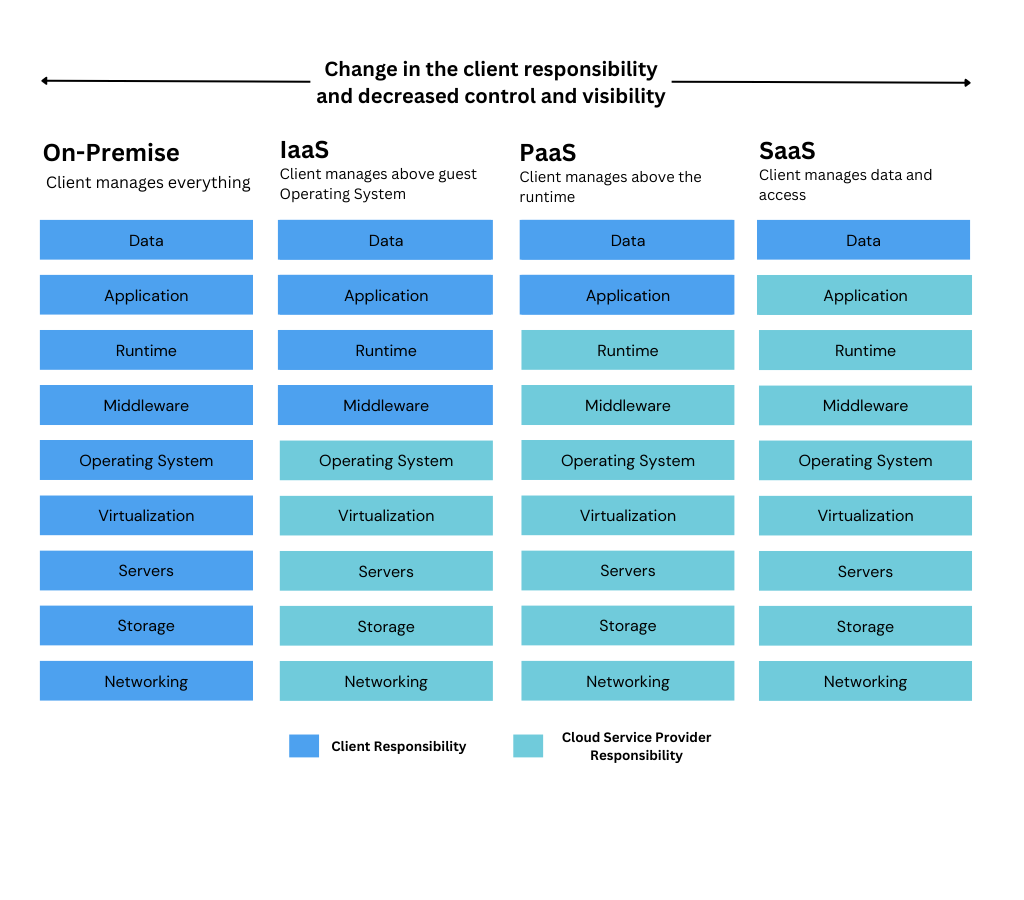
Shared and changing security responsibility
The image below demonstrates that security teams must now adjust to a shared responsibility model with their cloud service providers based on the available native cloud security features. This shift in responsibility for the enterprise exacerbates difficulties in achieving visibility and control in fragmented environments.
Building security in every stage of the cloud is a need.
Ensuring security throughout the business cloud migration process is critical for a successful hybrid multi-cloud environment. This approach differs from traditional security measures for on-premise environments. To achieve security in a hybrid multi-cloud, businesses must incorporate security considerations at every stage. This includes a continuous cycle of monitoring, security implementation, visibility of all assets, and security management.
Why Cloud Security is Important for Businesses
More than ever, businesses should adopt a cloud-first strategy to support business agility and resilience while quickening the process of digital transformation. Even though the cloud creates many new opportunities to update services and restructure operations, firms need help to achieve maximum ROI, primarily due to security and compliance constraints. These difficulties operate as significant barriers to a cloud-first journey when combined with the challenges in proactively addressing the complexity of a secure configuration and the lack of the necessary skill sets. Here are some reasons why cloud security is crucial for businesses now.
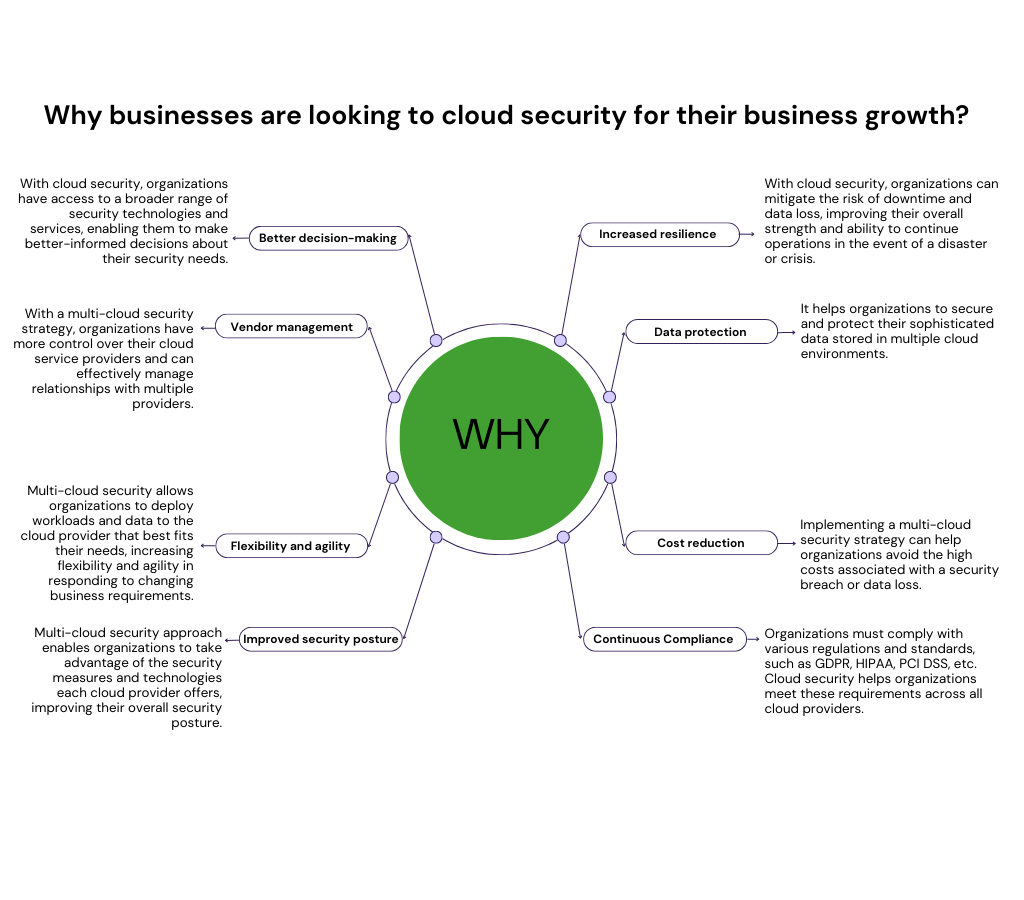
Cloud security prevents compassionate business, creative works, and consumer information from being exposed—either through unintentional breaches or sophisticated cyber-attacks—as more and more enterprises migrate to the cloud, with the industry anticipated to be worth $832.1 billion by 2025.
Because security is ingrained in the modern cloud, businesses may safeguard themselves from suffering significant losses or penalties due to breaking new and growing rules and regulations.
The certainty of cloud security will encourage businesses on the fence about shifting to the cloud to do so and take advantage of the many advantages of the cloud for long-term success and growth.
Since resources are constantly tracked and monitored, organizations can act on warning signs before they affect the performance or functioning of systems and processes. Cloud security can secure the continuity of business event problem downtime.
Main Risks Associated with Cloud Computing Security
Cloud computing security's primary goal is to reduce the risks that organizations constantly confront and to guarantee business continuity even in the event of an attack.
The lack of distinct perimeters in the public cloud creates a fundamentally different security reality. Adopting modern cloud strategies like automated Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) techniques, distributed serverless architectures, and transient assets like functions as a Service and containers make this even more difficult.
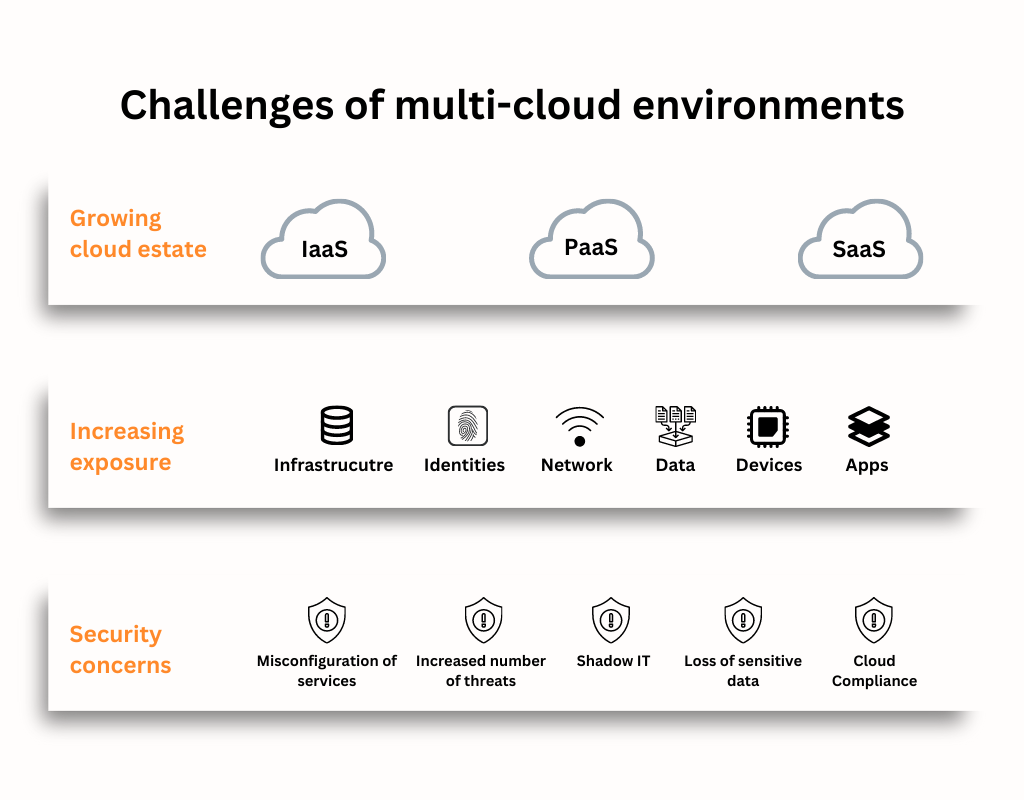
The various layers of risk and complicated cloud-native security challenges that today's cloud-oriented enterprises must deal with include:
Cloud Misconfiguration - One potential issue that can arise when a company moves its workloads to the cloud is the improper setup of security and privacy settings, and the training provided by vendors before migration may need to be revised for the complex tasks involved in configuring certain cloud services.
Increased Attack Surface - Hackers now use the public cloud environment as a large and very appealing attack surface, taking advantage of unsecured cloud ingress ports to access and disrupt workloads and data in the cloud. Many malicious dangers have entered daily life, including malware, zero-day vulnerabilities, account takeovers, etc.
Lack of visibility is a significant issue with cloud security, particularly in multi-cloud environments. Using third-party cloud providers may limit visibility into all layers of the cloud computing stack, making it difficult to identify security flaws or vulnerabilities.
Shadow IT - Bring-Your-Own-Cloud, also known as shadow IT or BYOC, is the term used to describe any software, hardware, or other systems utilized inside of a company but not supported by the IT staff, such as unauthorized apps, etc. Any company that doesn't pass them could be subject to significant security risks from these apps and solutions. A study from EMC suggests that data loss and downtime because of Shadow IT result in losses of $ 1.7 trillion each year.
Cloud Compliance - Most enterprises need adherence to various data privacy laws and industry standards. However, creating and enforcing compliance regulations for cloud systems is considerably complex. That is why organization faces challenges such as Lack of Staff Knowledge and Expertise, Complex Audits, Compliance Monitoring, Changing requirements, Cloud Vulnerability Management, and Compliance Automation. CSA's Sensitive Data in the Cloud Report revealed that over two-thirds (67%) of respondents now store sensitive data or workloads with public cloud service providers (CSPs).
Unsecured APIs - The cloud presents a challenge since attackers have many potential entry routes. The surface attack area is much more widespread, although it may be smaller overall. The growing popularity of serverless operations and micro-service architecture best illustrates this. Intruders can steal data by breaking into less secure APIs.
Open Source - Use of an open source in application development. Open-source software packages are weak. The majority of the time, hackers contaminate the Git repository. At the same time, they wait for developers to use the packages to breach the application via a well-planned attack vector eventually.
Identity and access control - Every organization's comprehensive security strategy is identity and access management (IAM). Effective businesses ensure regulatory compliance and risk management drivers are balanced with business-friendly and efficient processes to give users access to the appropriate resources at the proper time. 61% of all breaches involve credentials, whether stolen via social engineering or hacked using brute force.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Security?
24×7 Visibility - Cloud security platforms monitor cloud-based assets and applications round-the-clock. This enables firms to monitor their risk posture and its effects on their operations.
Adequate protection against DDoS Attacks - Cloud security offers the most effective defence against DDoS attacks, which are growing in frequency, scale, sophistication, and intensity. Cloud computing security continuously monitors, analyzes, and mitigates DDoS attacks. Such solutions can fend off volumetric, low-level, and sluggish attacks thanks to their built-in redundancies, customization options, flexibility, scalability, and intelligence.
Data Security - It is built into the top cloud computing security solutions. They have security methods and policies to stop unwanted parties from obtaining private data, such as strict access controls and data encryption.
Advanced Threat Detection - Cloud computing security can quickly identify attacks using endpoint scanning and global threat intelligence. This aids in determining the threats to the organization's mission-critical assets concerning the threat environment.
Regulatory Compliance - Excellent cloud application security vendors support adherence to legal and industry compliance requirements. It accomplishes this through managed security services and improved infrastructure.
What kinds of tools are required to secure a cloud environment?
Secure a cloud environment by using the security tools provided by each cloud service or deploying a centralized cloud unified security management tool that offers orchestration and secures all services from a single console. The latter approach is the most effective and long-term solution for connecting cloud environment.
It encompasses multiple security tools on one platform.
Reduced IT overhead through automated workflows.
Proactive security measures for cloud configuration issues.
Simplified Cloud Security Posture Management.
Enable Zero Trust Entitlement.
Data first security across Hybrid Data Technologies.
Compliance security, Advanced SecOps with Incident Management System.
Discovery of assets Adequate remediation at your fingertip information, Security check Visualization.
What are cloud security best practices?
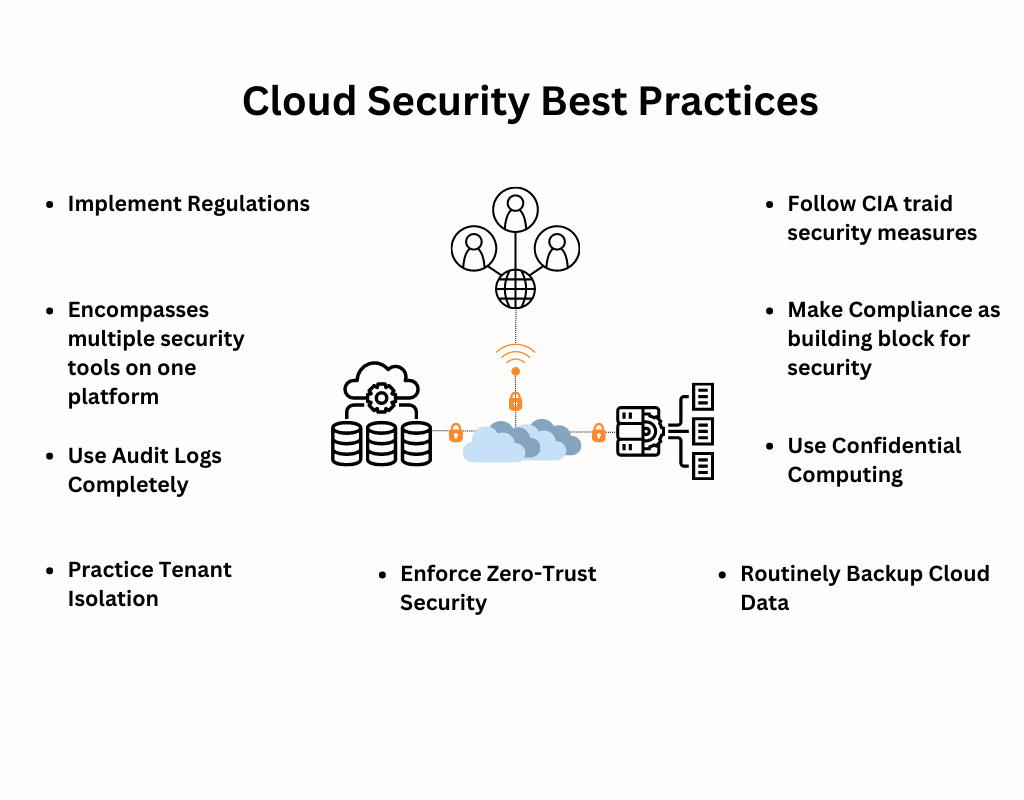
Clarify security responsibilities by understanding the shared responsibility model and cloud provider's security tools.
Establish comprehensive monitoring through integrating different tools across cloud providers.
Implement consistent policies across all cloud platforms.
Use automation to save time and reduce human error.
Centralize security management through a single dashboard.
Maintain conformity in security measures across the entire cloud infrastructure.
Implement a security tool that helps IT, SecOps, and Development teams
collaborate most efficiently by offering simplified Security Posture non-compliant alerts to protect the enterprise production environment.
Future of cloud
The future of cloud computing is shifting towards a multi-cloud (or hybrid cloud) approach as part of digital transformation efforts. Hence, the end of cloud security will also involve securing multi-cloud environments. As the attack surface grows and attacks become more advanced, organizations with intricate cloud setups must adopt multi-cloud security measures to ensure protection.
Simplifying security in complex cloud setups is the ultimate goal of cloud security
Securing a diverse cloud infrastructure is crucial. However, it is a challenging task as standards are yet to be established, and there is no collaboration between significant cloud providers. A robust cloud security solution enables the security team to address the limitations created by cloud providers, making it easier to identify problems, track service performance, detect potential threats, and resolve issues promptly.
