How Cloud Computing Accelerated Digital Transformation? And Challenges It Is Facing Now
Digital transformation evolution made data one of the most critical factors in the digital era. Companies use gigantic amounts of data to identify trends, benchmark against competitors, and track prior achievements and failures. Data was used to present and informing stakeholders how the company's performance. However, data can offer much more than that in the technologically sophisticated environment of today. It can determine and uncover a customer’s purchase patterns, budget, growth predictions, profit, etc.
To save large amounts of data and process it efficiently, companies started using a new technology called “Cloud Storage”. Cloud storage is a cloud computing model that delivers a more affordable, scalable interface alternative to storing on hard drives or storage networks.
Computer hard drives can only store a limited amount of data. Cloud storage services provide elasticity, which means the business can scale capacity as data volume increases. When digital transformation adopted the cloud it changed the gears in technology. By storing data in a cloud, organizations save by paying for storage technology rather than investing in the capital costs of building and maintaining in-house storage networks.
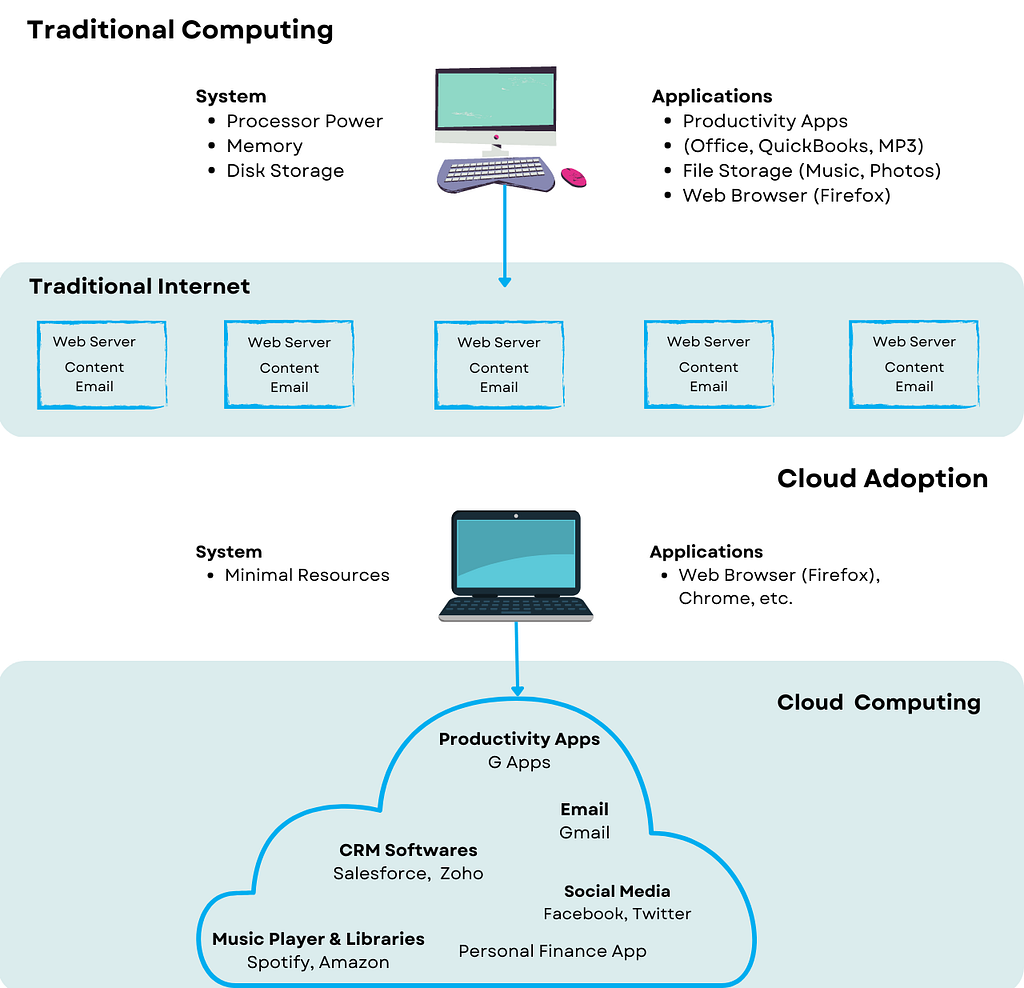
In this digital age, any firm's breadth of digital transformation goes beyond just converting paper-based record-keeping procedures to digital files. Businesses can modify their procedures to engage customers more naturally, thanks to digital devices, apps, storage, and other tools.
Large projects are accomplished without relying on on-site IT support.
Even though it is available to everybody who wants it, data is still protected.
Cloud adoption became the main pillar of Digital Transformation
The efficiency of the IT infrastructure depends on how well it is planned. It might be difficult for an organization to take advantage of new prospects with a traditional infrastructure. Whether businesses are expanding their healthcare infrastructure, providing customers with new material to stream, using robots in their warehouses, or opening their following cloud-based quick service restaurants. The cloud is the engine for all potential new businesses.
Regardless of the goals of digital transformation, adopting the cloud is a requirement for business transformation. The cloud adoption model opens up cost-saving innovation opportunities by enabling the syncing of current and old systems, extending the reach of products and services, and creating extremely resilient business models. Organizations use cloud computing platforms to function at scale and provide customer value.
Any size of business must be able to adapt to the digital era using the new services created by cloud-powered digital transformation.
Cloud-Enabled Services: Methods to digital transformation
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS)
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): It's a pay-as-you-need service where a third party gives businesses internet-based infrastructure services like virtualization and storage as they need.
Businesses need to take responsibility for the operating system, data, applications, middleware, and runtimes as the user. A provider offers access to and administration over the network, servers, virtualization, and storage they require.
Platform as a service (PaaS): It is another step further from complete, on-premise infrastructure management. It is where a provider hosts the hardware and software on its infrastructure and delivers this platform to the user as an integrated solution, solution stack, or service through an internet connection.
Primarily useful for developers and programmers, PaaS allows users to develop, run, and manage their apps without building and maintaining the infrastructure or platform usually associated with the process.
Software as a service (SaaS): It is the complete type of cloud computing service, delivering an entire application that a provider controls via a web browser.
The user connects to the app through a dashboard or API, and the provider manages software upgrades, bug patches, and general software maintenance. A group can access the application more easily and reliably without requiring individual computers to install the software.

Examples of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
Platforms | Example |
PaaS | AWS Elastic, Google App Engine, and Adobe Tools |
SaaS | Gmail, Banyan Cloud, and Microsoft Office 365 |
IaaS | AWS, GCP, Microsoft Azure |
Challenges in Cloud Adoption
It can be challenging to make the appropriate choice because so many operational and cyber security technologies are comparable.
Data security is their top worry when businesses store sensitive data with a third-party cloud provider. Data loss, leakage, or exposure might seriously disrupt operations and harm the company.
Moving to the cloud has many advantages, but getting it is typically costly and time-consuming.
Processes for cloud migration still need to be comprehended and used. Furthermore, many businesses still need to be more concerned about the need for more knowledge and training resources.
Cloud environments are complex to manage and take time to understand.
Moving to the cloud can be challenging for businesses operating under rigorous regulatory and compliance frameworks.
For many businesses, downtime may be disastrous in terms of income and reputation.

Digital Supply Chain Risk - Cybercriminals have found attacks against the digital supply chain to have a significant return on investment. More dangers are anticipated as vulnerabilities like Log4j increase throughout the supply chain. According to Gartner. 45% of organizations globally are expected to have experienced attacks on their software supply chain by 2025.
Identity System Security - Credential misuse is now a major attack vector due to sophisticated threat actors actively targeting identity and access control infrastructure.
Surface Attack Expansion - The attack surface of enterprises is growing. Using open-source code, cloud apps, complicated digital supply chains, social media, and other technologies has exposed organizations to risks outside controllable assets.
Human Error - Many data breaches still include human mistakes, which shows that conventional security awareness training methods are unsuccessful. According to an IBM report, 23% of all data breaches result from human error.
Distributed Decision - Executives need more agile security in the face of a growing attack surface as enterprise cybersecurity expectations and need mature. Due to the size, scope, and complexity of digital business, security decisions get distributed across different organization departments, making it hard to agree on one point.
Cloud adoption was the next and necessary step in digital transformation to make it more advanced, easy, and accessible to people and businesses. because of cloud adoption, many cloud security challenges arose in and this made organizations vulnerable and open to cyberattacks by threats and hackers.
